530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
给你一棵所有节点为非负值的二叉搜索树,请你计算树中任意两节点的差的绝对值的最小值。
示例:
输入:
1
\
3
/
2
输出:
1
解释:
最小绝对差为 1,其中 2 和 1 的差的绝对值为 1(或者 2 和 3)。
提示:
- 树中至少有 2 个节点。
- 本题与 783. 二叉搜索树节点最小距离 相同
思路
- 利用搜索二叉树的特性,最小绝对差一定位每个节点和其左子树最右节点的差值以及右子树的最左节点的差值之中,利用该特性递归解决即可。
- 搜索二叉树的特性是中序遍历单调递增,所以最小差值一定在中序遍历时相邻两个节点的差值。
解法
1. 中序遍历
利用中序遍历的特性获取当前节点与前一个节点的差值。
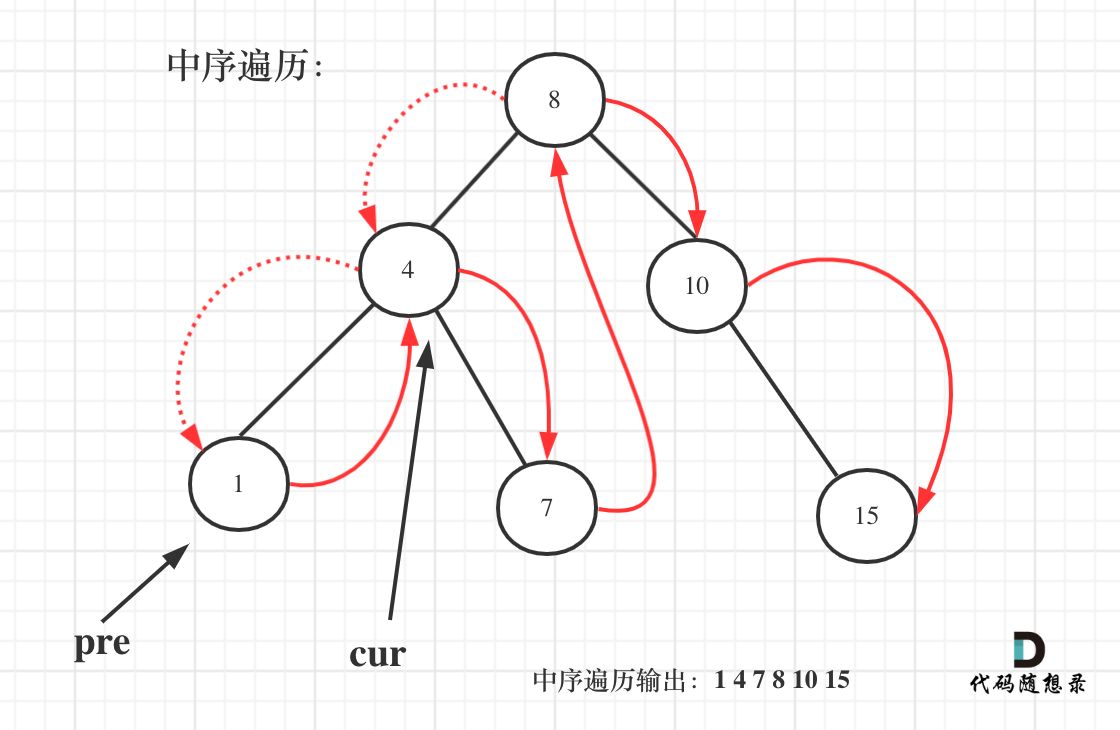
class Solution {
TreeNode pre;// 记录上一个遍历的结点
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
// 左
int left = getMinimumDifference(root.left);
// 中
if (pre != null) {
result = Math.min(left, root.val - pre.val);
}
pre = root;
// 右
int right = getMinimumDifference(root.right);
result = Math.min(right, result);
return result;
}
}
2. 常规递归
递归维护每个节点的最小差值
class Solution {
int minDiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode node = root;
if (root.left != null) {
node = root.left;
while (node.right != null) {
node = node.right;
}
minDiff = Math.min(minDiff, root.val - node.val);
minDiff = Math.min(minDiff, getMinimumDifference(root.left));
}
if (root.right != null) {
node = root.right;
while (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
}
minDiff = Math.min(minDiff, node.val - root.val);
minDiff = Math.min(minDiff, getMinimumDifference(root.right));
}
return minDiff;
}
}