513. 找树左下角的值
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
示例 1:
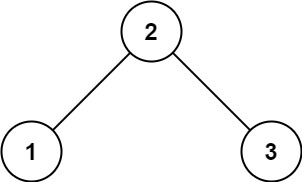
输入: root = [2,1,3]
输出: 1
示例 2:
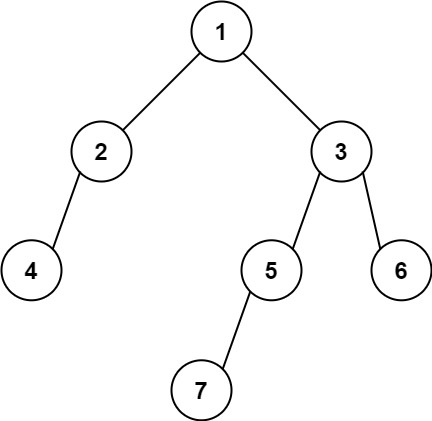
输入: [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7]
输出: 7
提示:
- 二叉树的节点个数的范围是
[1,104] -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
解法
1. 层序遍历BFS
使用层序遍历保存每一行的第一个值,然后又把最后一行的第一个值返回即可。
class Solution {
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
ArrayDeque<TreeNode> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.offer(root);
int result = 0;
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
int len = deque.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
TreeNode node = deque.poll();
if (i == 0) {
//保存每一行的第一个值
result = node.val;
}
if (node.left != null) {
deque.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
deque.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
2. 递归DFS
使用递归的话需要维护二叉树的当前节点深度和最大节点深度,遍历过程中要先遍历左节点,这样当深度增加的时候保存第一个节点的值即可。
class Solution {
int result = 0;
int maxDepth = -1;
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
traversal(root, 0);
return result;
}
public void traversal(TreeNode root, int curDepth) {
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if (curDepth > maxDepth) {
maxDepth = curDepth;
result = root.val;
}
}
if (root.left != null) {
traversal(root.left, curDepth + 1);
}
if (root.right != null) {
traversal(root.right, curDepth + 1);
}
}
}