148. 排序链表
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
示例 1:
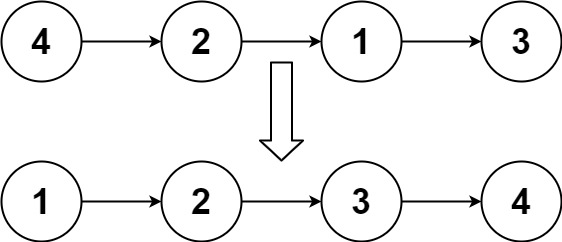
输入:head = [4,2,1,3]
输出:[1,2,3,4]
示例 2:
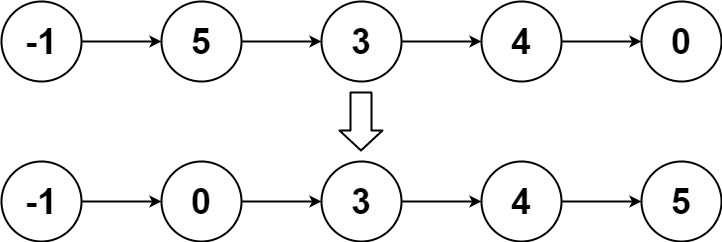
输入:head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
输出:[-1,0,3,4,5]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 5 * 10^4]内 -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
进阶:你可以在 O(nlogn) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序吗?
解法
既然题目要求 O(nlogn) 时间复杂度,那么像是冒泡、插入等排序方法可以直接放弃。可以尝试使用归并排序或者快速排序。
1. 归并排序(递归)
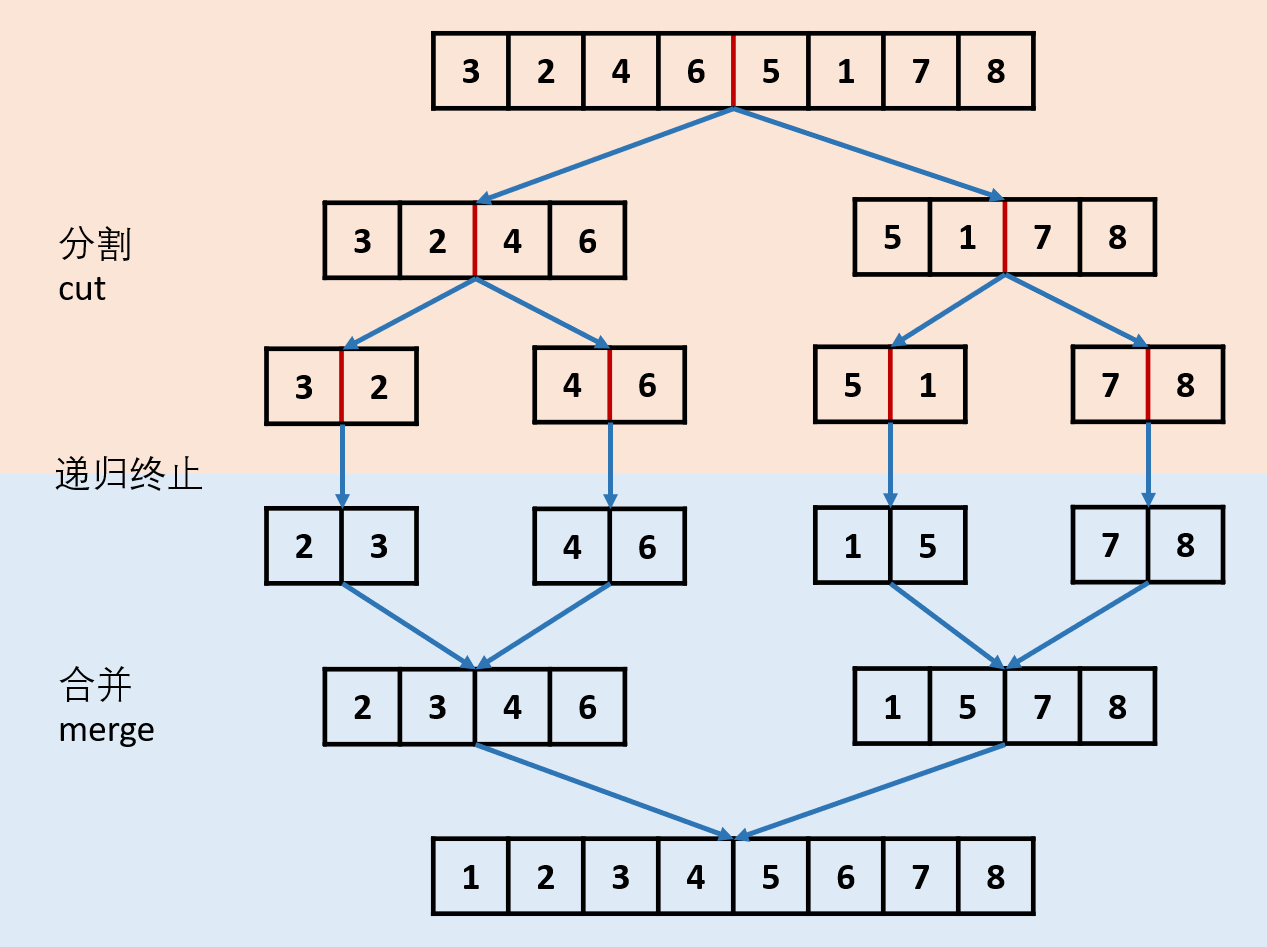
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 通过快慢指针将链表二等分
ListNode fast = head.next;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode tmp = slow.next;
// 截断链表
slow.next = null;
// 递归处理左右两部分
ListNode left = sortList(head);
ListNode right = sortList(tmp);
// 归并两部分链表
ListNode newHead = merge(left, right);
return newHead;
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
ListNode cur = new ListNode();
ListNode newHead = cur;
while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {
if (head1.val <= head2.val) {
cur.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
} else {
cur.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = head1 != null ? head1 : head2;
return newHead.next;
}
}
2. 归并排序(迭代)
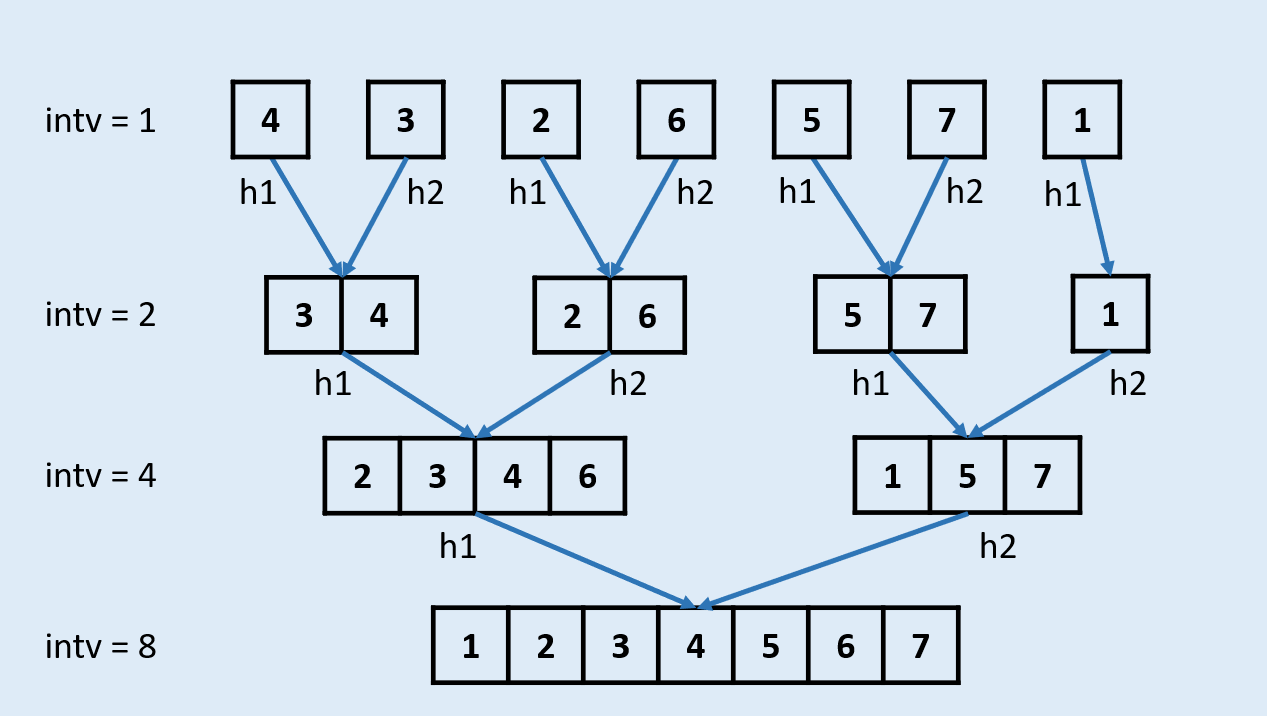
//TODO
3. 快速排序
快速排序,借助临时链表,如果当前元素小于基准,就加入临时链表,并在原链表中删除,最后再连接上未被删除的元素。参照 86. 分隔链表。
链表太长时会超时。
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
// 边界
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
// 伪头结点
ListNode pre = new ListNode(0, head);
// 快排
quickSort(pre, null);
// 返回头结点
return pre.next;
}
public void quickSort(ListNode pre, ListNode end) {
if (pre == end || pre.next == end || pre.next.next == end) {
return;
}
ListNode pivot = partition(pre, end);
// 递归处理
quickSort(pre, pivot);
quickSort(pivot, end);
}
// 输入伪头结点和尾节点null,借助临时链表进行处理
public ListNode partition(ListNode pre, ListNode end) {
// 选第一个节点为基准
ListNode pivot = pre.next;
// 建立临时链表
ListNode cur = new ListNode(0);
// 临时左右两指针
ListNode r = pivot, l = cur;
// 遍历,右指针下一节点为end,说明当前是最后一个元素,结束
while (r.next != end) {
// 如果当前元素小于基准,就加入临时链表,并在原链表中删除
if (r.next.val < pivot.val) {
l.next = r.next;
l = l.next;
r.next = r.next.next;
} else {
// 不小于基准,右指针后移
r = r.next;
}
}
// 临时链表接在原链表前面,并把伪头结点指向临时节点头结点
l.next = pre.next;
pre.next = cur.next;
return pivot;
}
}