111. 二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
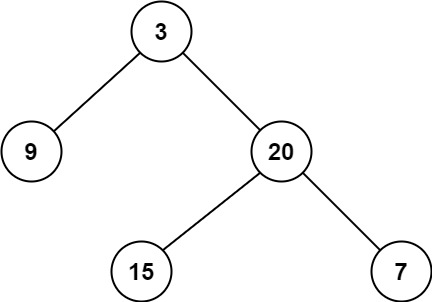
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
输出:5
提示:
- 树中节点数的范围在
[0, 105]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
思路
BFS遍历,遇到叶子节点则终止并返回当前深度。
递归思路个陷阱。
解法
1. 迭代
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
ArrayDeque<TreeNode> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
int levelSize = 0;
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
levelSize = deque.size();
depth++;
while (!deque.isEmpty() && levelSize > 0) {
root = deque.poll();
//叶子节点
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return depth;
}
if (root.left != null) {
deque.offer(root.left);
}
if (root.right != null) {
deque.offer(root.right);
}
levelSize--;
}
}
return depth;
}
}
2. 递归
这块和104题求最大深度可就不一样了,一些同学可能会写如下代码:
int leftDepth = getDepth(node.left);
int rightDepth = getDepth(node.right);
int result = 1 + Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth);
return result;
这个代码就犯了此图中的误区:
如果这么求的话,没有左孩子的分支会算为最短深度。
所以,如果左子树为空,右子树不为空,说明最小深度是 1 + 右子树的深度。
反之,右子树为空,左子树不为空,最小深度是 1 + 左子树的深度。 最后如果左右子树都不为空,返回左右子树深度最小值 + 1 。
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = minDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = minDepth(root.right);
if (root.left != null && root.right == null) {
return leftDepth + 1;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right != null) {
return rightDepth + 1;
}
return Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
}