86. 分隔链表
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个特定值 x ,请你对链表进行分隔,使得所有 小于 x 的节点都出现在 大于或等于 x 的节点之前。
你应当 保留 两个分区中每个节点的初始相对位置。
示例 1:
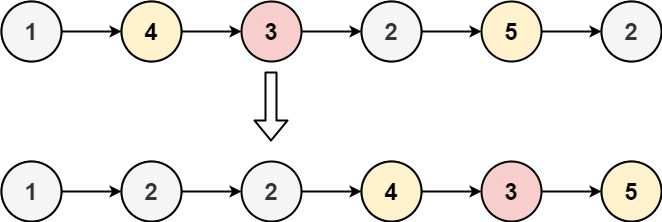
输入:head = [1,4,3,2,5,2], x = 3
输出:[1,2,2,4,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [2,1], x = 2
输出:[1,2]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 200]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100-200 <= x <= 200
解法
1 拆分成两个链表
将值大于等于 x 的节点从原链表删除在拼接成一个新的链表,最后将原链表和新链表相连。
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 小于 x 的节点放在 headA,大于等于 x 的节点放在 headB
ListNode headA = new ListNode(), headB = new ListNode();
headA.next = head;
ListNode curA = headA, curB = headB;
while (curA.next != null) {
if (curA.next.val < x) {
curA = curA.next;
continue;
}
curB.next = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
curA.next = curA.next.next;
curB.next = null;
}
// headA 尾部连接 headB
curA.next = headB.next;
return headA.next;
}
}
2 双指针原地调整
左指针始终指向 < x 的最后一个节点,右指针向右遍历
- 如果右指针遇到
>= x的节点,继续移动 - 如果右指针遇到
< x的节点,将其移动到左指针的下一位且左指针后移一位。
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode left = dummyHead;
// 左指针先移动到 < x 的节点的末尾
while (left.next != null && left.next.val < x) {
left = left.next;
}
if (left.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 右指针开始遍历
ListNode right = left.next;
while (right.next != null) {
while (right.next != null && right.next.val >= x) {
right = right.next;
}
// 将当前节点移动到左节点后面
move(left, right);
left = left.next;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
public void move(ListNode left, ListNode right) {
if (right.next == null) {
return;
}
ListNode moveNode = right.next;
right.next = right.next.next;
moveNode.next = left.next;
left.next = moveNode;
}
}
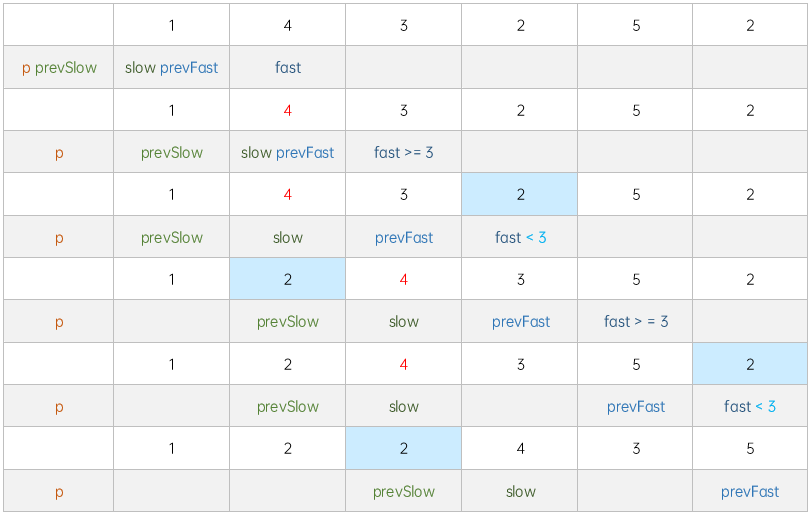
3 双指针另一种写法
慢指针只在 < 目标值移动,快指针始终移动
慢指针停在 >= 目标值时,如果快指针 < 目标值,移动快指针节点到慢指针节点前
- 删除:快指针
上节点→ 快指针下节点 - 插入:慢指针
上节点→ 快指针节点→ 慢指针节点
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(), prevSlow = dummyHead, slow = head, prevFast = head, fast = head.next;
prevSlow.next = head;
// 慢指针只在 < x 时移动,快指针始终移动
// 慢指针停在 >= x 时,如果快指针 < x,移动快指针节点到慢指针节点前
// 1. 删除:快指针 pre 节点 → 快指针next节点
// 2. 插入:慢指针 pre 节点 → 快指针节点 → 慢指针节点
while (fast != null) {
if (slow.val < x) {
// 先移动到分界点
prevSlow = slow;
slow = slow.next;
prevFast = fast;
} else if (fast.val < x) {
// 删除节点
prevFast.next = fast.next;
// 移动到 prevSlow 后面
prevSlow.next = fast;
fast.next = slow;
prevSlow = fast;
} else {
// fast.val >= x 向右移动
prevFast = fast;
}
fast = prevFast.next;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}