40. 组合总和 II
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
注意:解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8,
输出:
[
[1,1,6],
[1,2,5],
[1,7],
[2,6]
]
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5,
输出:
[
[1,2,2],
[5]
]
提示:
1 <= candidates.length <= 1001 <= candidates[i] <= 501 <= target <= 30
思路
本题在整体思路上和39. 组合总和相同,但本题的难点在于区别集合(数组candidates)有重复元素,但还不能有重复的组合。要对最终结果做去重处理。
一些同学可能想了:我把所有组合求出来,再用set或者map去重,这么做很容易超时!
所以要在搜索的过程中就去掉重复组合。
很多同学在去重的问题上想不明白,其实很多题解也没有讲清楚,反正代码是能过的,感觉是那么回事,稀里糊涂的先把题目过了。
这个去重为什么很难理解呢,所谓去重,其实就是使用过的元素不能重复选取。 这么一说好像很简单!
都知道组合问题可以抽象为树形结构,那么“使用过”在这个树形结构上是有两个维度的,一个维度是同一树枝上使用过,一个维度是同一树层上使用过。没有理解这两个层面上的“使用过” 是造成大家没有彻底理解去重的根本原因。
那么问题来了,我们是要同一树层上使用过,还是统一树枝上使用过呢?
回看一下题目,元素在同一个组合内是可以重复的,怎么重复都没事,但两个组合不能相同。
所以我们要去重的是同一树层上的“使用过”,同一树枝上的都是一个组合里的元素,不用去重。
为了理解去重我们来举一个例子,candidates = [1, 1, 2], target = 3,(方便起见candidates已经排序了)
强调一下,树层去重的话,需要对数组排序!
选择过程树形结构如图所示:
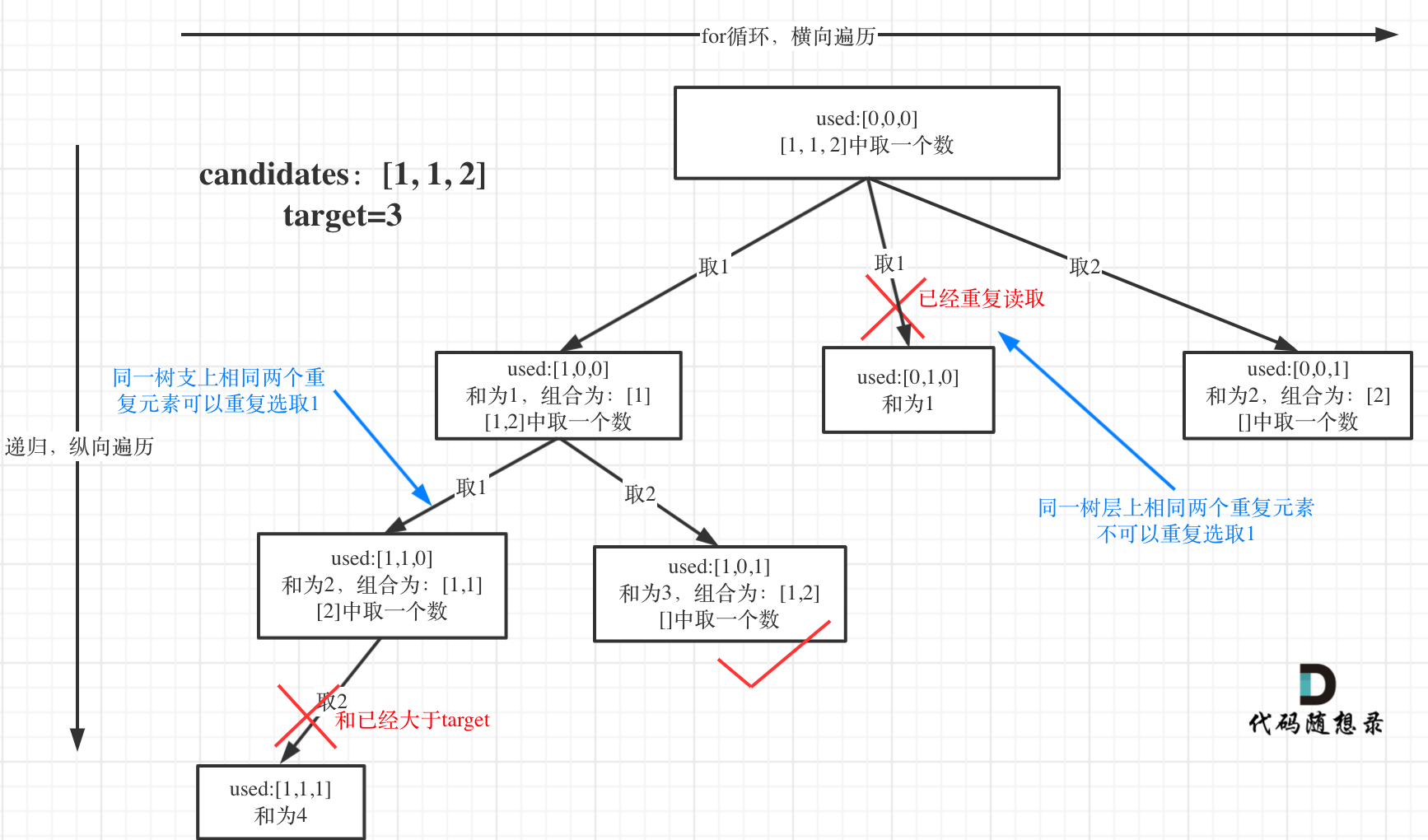
可以看到图中,每个节点相对于 39.组合总和 我多加了used数组,这个used数组下面会重点介绍。用来记录同一树枝上的元素是否使用过。这个集合去重的重任就是used来完成的。
前面我们提到:要去重的是“同一树层上的使用过”,如果判断同一树层上元素(相同的元素)是否使用过了呢。
如果candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] 并且 used[i - 1] == false,就说明:前一个树枝,使用了candidates[i - 1],也就是说同一树层使用过candidates[i - 1]。
此时for循环里就应该做continue的操作。
这块比较抽象,如图:
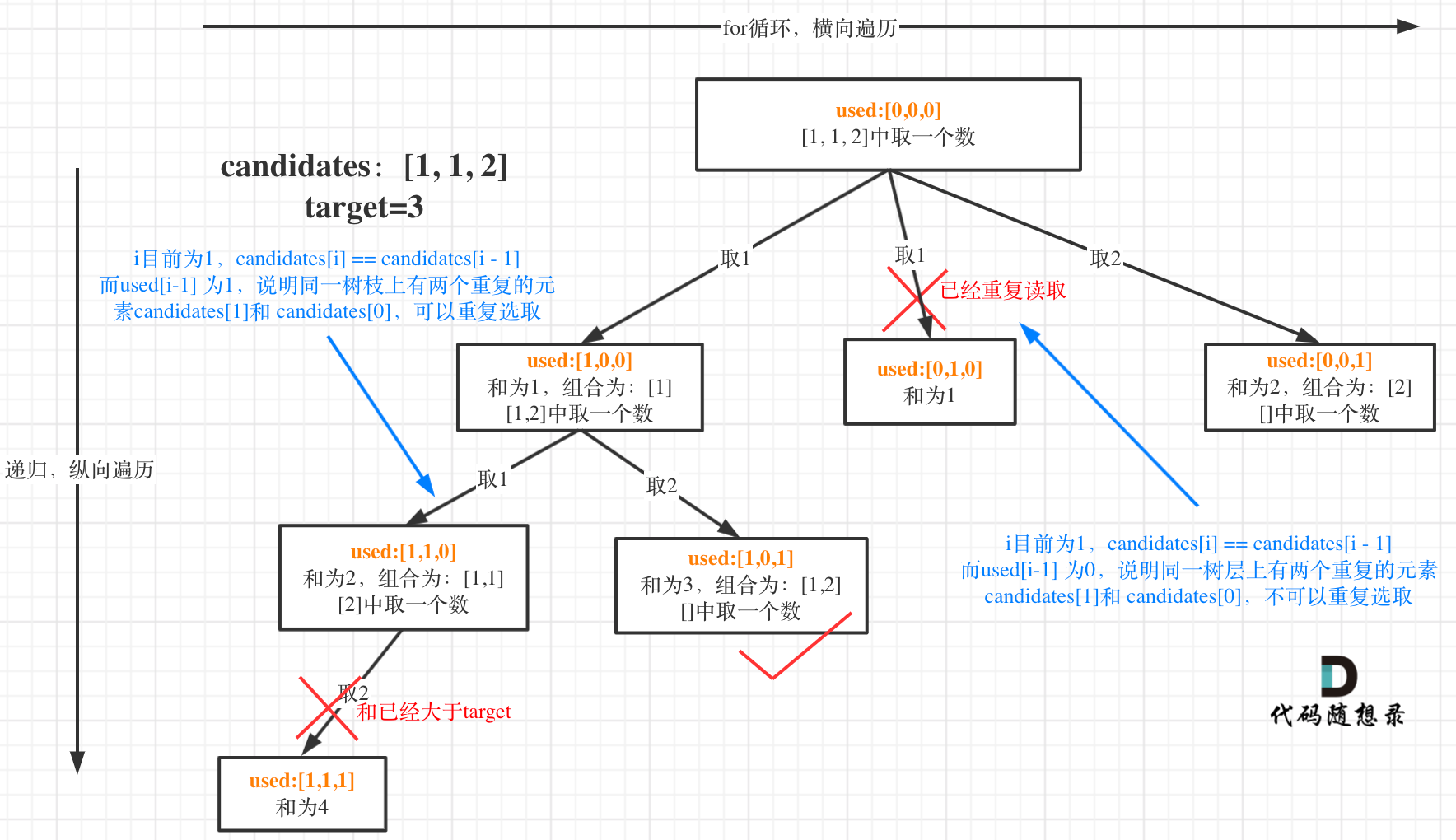
我在图中将used的变化用橘黄色标注上,可以看出在candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]相同的情况下:
- used[i - 1] == true,说明同一树支candidates[i - 1]使用过
- used[i - 1] == false,说明同一树层candidates[i - 1]使用过
解法
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
if (candidates == null || candidates.length == 0) {
return result;
}
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backtracking(candidates, target, 0);
return result;
}
public void backtracking(int[] candidates, int target, int start) {
if (target == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
return;
}
//判断该位置上的数据是否使用过
boolean[] uesd = new boolean[candidates.length - start];
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length && target - candidates[i] >= 0; i++) {
uesd[i - start] = true;
if (i > start && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && uesd[i - start - 1]) {
// 当前数据和前一个数据相等,且已经选去过前一个数据,直接跳过
continue;
}
list.add(candidates[i]);
backtracking(candidates, target - candidates[i], i + 1);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
}
}
}